Bladder scanners are specialized ultrasound devices used to measure the volume of the bladder. It is a game-changing technology that offers an accurate, non-invasive way of bladder scanning, ensuring optimal patient care.
According to Mordor Intelligence, the Bladder Scanners Market is expected to grow from USD 159.66 million in 2024 to USD 214.67 million by 2029, experiencing a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.10% throughout the forecast period of 2024 to 2029.
In today’s blog, we will explore all about bladder scanners, how they work, best practices for using these scanners, and much more.
What are Bladder Scanners?
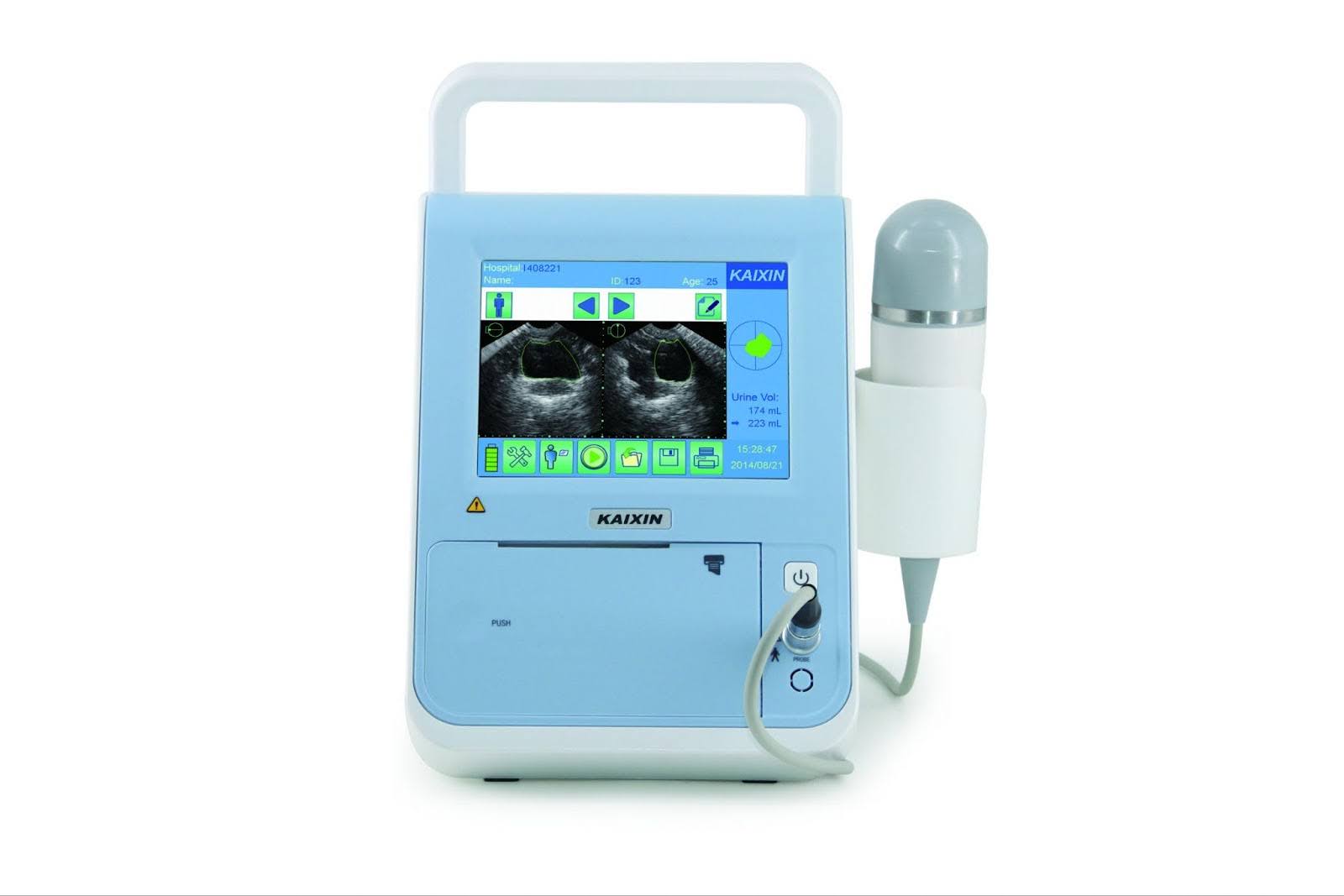
Image: Source
A bladder scanner is a portable ultrasound equipment that offers instant and accurate measurement of the bladder’s volume. The technology behind the scanner hinges on the use of ultrasound ways, which are transmitted into the body. These waves echo off the bladder and are precisely captured by the scanner to determine the shape and size of the bladder.
Once the measurements are obtained, advanced algorithms calculate the exact volume of urine present in the bladder. This information is then displayed on a screen for healthcare professionals to interpret and make informed decisions regarding patient care.
An increasing number of healthcare professionals are using bladder scanners to diagnose urinary retention and decide whether catheterization is required or not.
Benefits of Using Bladder Scanners
Using bladder scanners offers a plethora of benefits for both patients and healthcare professionals. The most notable ones are mentioned below:
- Safe and Non-Invasive: Bladder scanners are considered absolutely safe and non-invasive. Unlike catheterization, they do not pose a risk of infection.
- Accurate Bladder Volume Assessment: Bladder scanners offer a precise measurement of the bladder’s volume. This helps healthcare professionals determine the presence of urinary complications such as urine retention and suggest appropriate treatment.
- Portable and Easy to Use: Portable bladder scanners are available that come in various sizes, including handheld options that can be used at the point-of-care or even in home settings. The convenience offered by these devices promotes greater accessibility to accurate bladder measurements.
- Quick and Cost-Efficient Process: Using bladder scanners is a quick and time-efficient process. It eradicates the need for catheterization further promotes cost savings for hospitals and reduces waiting times for patients.
- Enhanced Patient Comfort: Bladder scanning safeguards the patient’s dignity and comfort as it is a non-invasive process. It also eliminates the chances of potential complications associated with the use of a catheter.
Applications of Bladder Scanners in Healthcare
Bladder scanners are widely used in various healthcare settings:
- Urology Clinics: Bladder scanners are used by urologists to diagnose and treat bladder issues such as bladder outlet obstruction. Based on the results, they may be able to provide suitable treatment plans.
Additionally, bladder scanners help urologists to determine the exact amount of residual urine in a patient’s bladder. This can guide them in determining whether catheterization is necessary or if alternative methods like medication or pelvic floor exercises are more suitable.
- Post-Operative Care: Doctors in many hospitals use bladder scanners post-operatively to continuously observe bladder volume and prevent urinary retention, which is a common post-surgical complication.
- Long-Term Care: Patients suffering from ailments such as neurogenic bladder can use bladder scanners to effectively manage their urinary conditions.
Steps to Use a Bladder Scanner
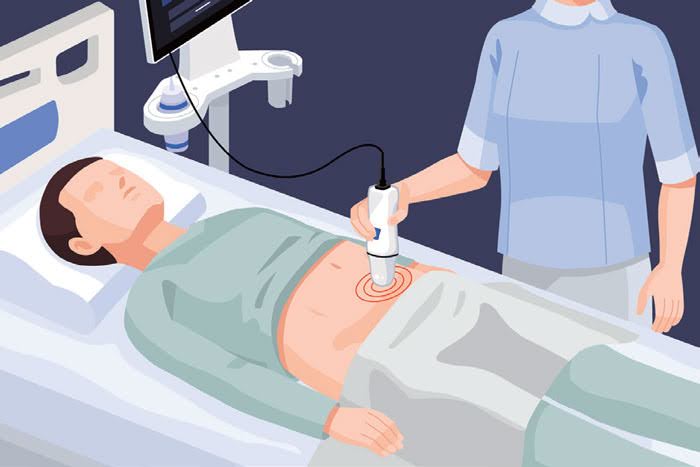
Image: Source
Using a bladder scanner is a straightforward process. Simply follow the below-mentioned steps for an accurate measurement of bladder volume.
- Turn on the bladder scanner by pressing the power button on the portable device.
- Next you need to add the patient data. Most scanners have a “Patient” button to access the patient management system. Click on it to select the patient’s gender.
- The next step involves preparing the patient. Have the patient lie down on their back and apply an ultrasound gel on the area to be scanned, i.e. around the abdomen.
- Put the scanning device, known as the probe, on the gel (ideally 3-5 cm from the pelvis). Press the probe button to initiate the pre-scan and locate the bladder. Gradually rotate the probe upwards so it directly faces the patient’s head. This will help to locate the bladder.
- Once the bladder is located, press the probe button again to initiate the scan. The scanner will automatically start calculating the bladder volume and Post-Void Residual (PVR). As you hear a beep, the results will be displayed on the monitor.
Once you have got the results, wipe the ultrasound gel off the patient and the probe.
Best Practices for Using a Bladder Scanner
Accurate bladder measurement is essential for assessing urinary retention and formulating effective treatment plans. For optimal bladder scanner use, make sure to adhere to the following best practices:
- Training is critical. Ensure that your staff is well-versed in the scanner’s functions and correct positioning on the patient’s abdomen to ensure precise readings.
- Hygiene is paramount. The probe must be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected before each use to avoid cross-contamination.
- For consistent results, patients should be encouraged to empty their bladders before scanning, and movement during the procedure should be minimized.
- Accurate documentation of data, including date, time, patient ID, and any observations, is crucial for tracking urinary health over time.
Following these guidelines helps healthcare professionals achieve accurate diagnostics and develop personalized care plans, thereby improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Bladder scanners have become invaluable in healthcare settings for accurately measuring bladder volume and improving patient care. These portable and handheld devices offer numerous benefits, including non-invasiveness, efficiency, and accuracy.
By providing healthcare professionals with real-time data on bladder volume, bladder scanners help prevent unnecessary catheterizations and reduce the risk of complications such as urinary tract infections.
Discover the future of non-invasive bladder health assessment with Santron Meditronic’s advanced Bladder Scanner technology. Connect with us today to explore how we can enhance your clinical practice.
FAQs Questions
Addressing common questions and concerns about uroflowmetry can enhance patient understanding and cooperation.
How does a bladder scanner work?
A bladder scanner emits ultrasound waves into the body, which bounce off the bladder and surrounding tissues. By analyzing the echoes of these waves, the scanner calculates bladder volume.
Are bladder scanners safe for patients?
Yes, bladder scanners are safe for patients, as they utilize non-invasive ultrasound technology without exposing patients to harmful radiation.
What factors can affect the accuracy of bladder scanner measurements?
Factors such as patient positioning, bladder shape, operator technique, and scanner calibration can influence the accuracy of bladder scanner measurements.
How often should bladder scanner calibration be performed?
Bladder scanner calibration should be performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations and institutional protocols, typically at regular intervals to ensure accuracy.
Can bladder scanners be used on pediatric patients?
Yes, bladder scanners can be used on pediatric patients, although adjustments may be needed to account for differences in anatomy and bladder size.
What are the potential limitations of bladder scanners?
Limitations of bladder scanners may include difficulty in obtaining accurate measurements in obese patients, patients with bladder abnormalities, or those with significant bowel gas.
Are there any special considerations for using bladder scanners in specific patient populations?
Special considerations may be necessary when using bladder scanners in pediatric patients, elderly patients, or those with certain medical conditions affecting bladder function.
Can bladder scanners be used in home healthcare settings?
While bladder scanners are primarily used in clinical settings, there are portable and handheld models suitable for home healthcare use, especially for patients requiring regular bladder volume monitoring.
How do bladder scanners compare to other methods of bladder volume measurement, such as catheterization or ultrasound?
Bladder scanners offer a non-invasive alternative to invasive procedures such as catheterization, providing accurate measurements without the associated risks of infection or discomfort. While ultrasound can also assess bladder volume, bladder scanners are specifically designed for this purpose, offering greater efficiency and ease of use.
What training is required for healthcare professionals to operate bladder scanners effectively?
Healthcare professionals should receive training on properly operating and using bladder scanners, including device setup, scanning techniques, result interpretation, and documentation procedures. Training may be provided by manufacturers or institutional educators, supplemented by ongoing competency assessments.

